Properties of Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Properties of CO2
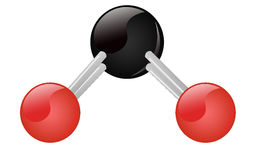
Physical properties of CO2 :-
Carbon dioxide is a colorless & odorless gas. It is soluble in water, ethanol , acetone and has the following properties :
- Melting Point : -55.6 degC
- Boiling Point : -78.5 degC
- Density : 1.977
Chemical properties of CO2 :-
- Carbon dioxide is a linear covalent molecule.
- Carbon dioxide is an acidic oxide and reacts with water to give carbonic acid.
- CO2 + H2O ==> H2CO3
- Carbon dioxide reacts with alkalis to give carbonates and bicarbonates.
- CO2 + NaOH ==> NaHCO3 (Sodium BiCarbonate )
- NaHCO3 + NaOH ==> Na2CO3 (Sodium Carbonate) + H2O
Uses of CO2
- It is used to neutralize alkaline water.
- Carbon dioxide is used as an additive to oxygen for medical use as a respiration stimulant
- Liquid Frozen Carbon Dioxide (Co2) is a good solvent for many organic compounds.
- Liquid Frozen Carbon Dioxide (Co2) is used as a propellant in aerosol cans, it replaces more environmentally troublesome alternatives
- It is used for refrigeration and cooling.
- It is used as an inert gas in chemical processes, in the storage of carbon powder and in fire extinguishers.
- It is used in solid as well as in liquid form
- It is used in metal industry in the formation of casting molds to enhance their hardness
- Carbon dioxide gas is used to carbonate soft drinks, beers and wine and to prevent fungal and bacterial growth.
- Large quantities are used as a raw material in the chemical process industry, especially for methanol and urea production.
- It is used in oil wells for oil extraction and maintain pressure within a formation
- Liquid or solid carbon dioxide is used for quick freezing, surface freezing, chilling and refrigeration in the transport of foods etc.
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) of CO2
Hazards Identification:
- Emergency Overview: Amber glass bottle packed inside a cardboard box. Clear, orange colored solution with camphor like odor. May cause eye irritation. For eyes-only.
- Eye: May cause temporary stinging, burning and conjunctival redness.
- Skin: May cause irritation, dermatitis and hypersensitivity in some individuals
- Ingestion: May cause irritation and hypersensitivity in some individuals. Will produce a yellow or green discoloration to the mouth.
- Inhalation: Aspiration of the medication may produce irritation and hypersensitivity in some individuals.
- Chronic Effects: Prolonged use may delay wound healing and is not recommended.
- Target Organs: Eyes, skin and central nervous system.
- Medical Conditions Aggravated by Long Term Exposure: This preparation should be used cautiously and sparingly in patients with cardiac disease, hypothyroidism or allergies.
First Aid Measures:
- Skin: Remove all contaminated clothing and wash skin with copious amounts of water for at least 20 minutes. Contact physician if skin becomes irritated.
- Eyes: Rinse immediately with copious amounts of water for at least 20 minutes. Contact a physician.
- Inhalation: Remove person to fresh air, and if breathing stops, use artificial respiration. Contact physician.
- Ingestion: Wash out mouth and drink plenty of water and bland fluids. The use of an emetic drug and/or gastric lavage is advisable. Do not give anything to an unconscious person. Contact physician.
Fire Fighting Measures:
- Hazardous Products: Emits toxic fumes, nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Fire Fighting Instructions: Wear self-contained breathing apparatus and protective clothing. Use water spray to keep fire-exposed containers cool. Do not spray water into the burning material.
- Extinguishing Media: Dry chemical, carbon dioxide, halon, water spray or fog, and foam on surrounding materials.
Accidental Release Measures
- Large/Small Spills: Use personal protective equipment. Contain the spill to prevent drainage into sewers, drains or streams. Use absorbent material to solidify the spill. Shovel up solidified waste.
Handling and Storage
- Handling: Avoid contact with product and use caution to prevent puncturing containers. No special protective equipment or procedures are required in the clinical or home environment.
- Storage: Store product upright in original containers with the cap tightly closed at a controlled room temperature 150-300 C (590- 860 F).
KEEP THIS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
----------------------------
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a colorless and odorless gas that is naturally present in the Earth's atmosphere. It is a greenhouse gas that plays a crucial role in regulating the planet's temperature. It is also widely used in various industries, including food and beverage, oil and gas, and medical. In this article, we will discuss the properties of carbon dioxide, including its physical, chemical, and molecular properties, as well as the properties of its solid form, dry ice.
CO2 Properties: Physical Properties
Carbon dioxide gas is denser than air and is soluble in water. Its density is about 1.98 kg/m3 at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. The gas is non-toxic, but at high concentrations, it can displace oxygen and cause suffocation. The melting point of CO2 is -78.5°C, and its boiling point is -56.6°C. These low melting and boiling points make CO2 an excellent coolant, and it is widely used in the food and beverage industry to freeze and transport perishable goods.
CO2 Properties: Chemical Properties
Carbon dioxide is a stable compound with the chemical formula CO2. It is not highly reactive and does not readily form chemical bonds with other substances. However, it can react with certain metals, such as magnesium, to form metal carbonates. Carbon dioxide is also slightly acidic and can react with water to form carbonic acid, which can corrode some metals and concrete.
CO2 Properties: Molecular Properties
The CO2 molecule consists of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. It has a linear shape, and the carbon-oxygen bonds are polar, with the oxygen atoms being slightly negative and the carbon atom being slightly positive. This polarity gives CO2 its unique properties, such as its solubility in water and its ability to absorb and re-emit infrared radiation, which contributes to the greenhouse effect.
CO2 Properties: Gas Properties
Carbon dioxide gas is not flammable, but it can act as an asphyxiant in confined spaces. It is also a good insulator and is used in some types of fire extinguishers to displace oxygen and smother flames. CO2 gas is also commonly used in beverage dispensing systems, where it is mixed with water or other liquids to create carbonated drinks.
Properties of Dry Ice (Solid CO2)
Dry ice is the solid form of CO2. It is created by cooling and compressing carbon dioxide gas, which causes it to condense into a solid form. Dry ice has a temperature of -78.5°C and is extremely cold. It is commonly used as a refrigerant in the food and beverage industry and can be used to freeze and transport perishable goods.
Dry ice is also used in theatrical productions and for special effects, as it produces a thick, white fog when it is exposed to air. However, it is essential to handle dry ice with care, as it can cause frostbite and skin damage if it comes into direct contact with the skin.
Conclusion
In conclusion, carbon dioxide is a stable compound with unique physical, chemical, and molecular properties. It is widely used in various industries, including food and beverage, oil and gas, and medical. Its solubility in water, ability to absorb and re-emit infrared radiation, and low melting and boiling points make it a versatile and valuable compound. The solid form of CO2, dry ice, is also widely used as a refrigerant and for special effects. However, it is important to handle dry ice with care, as it can cause skin damage and frostbite.
